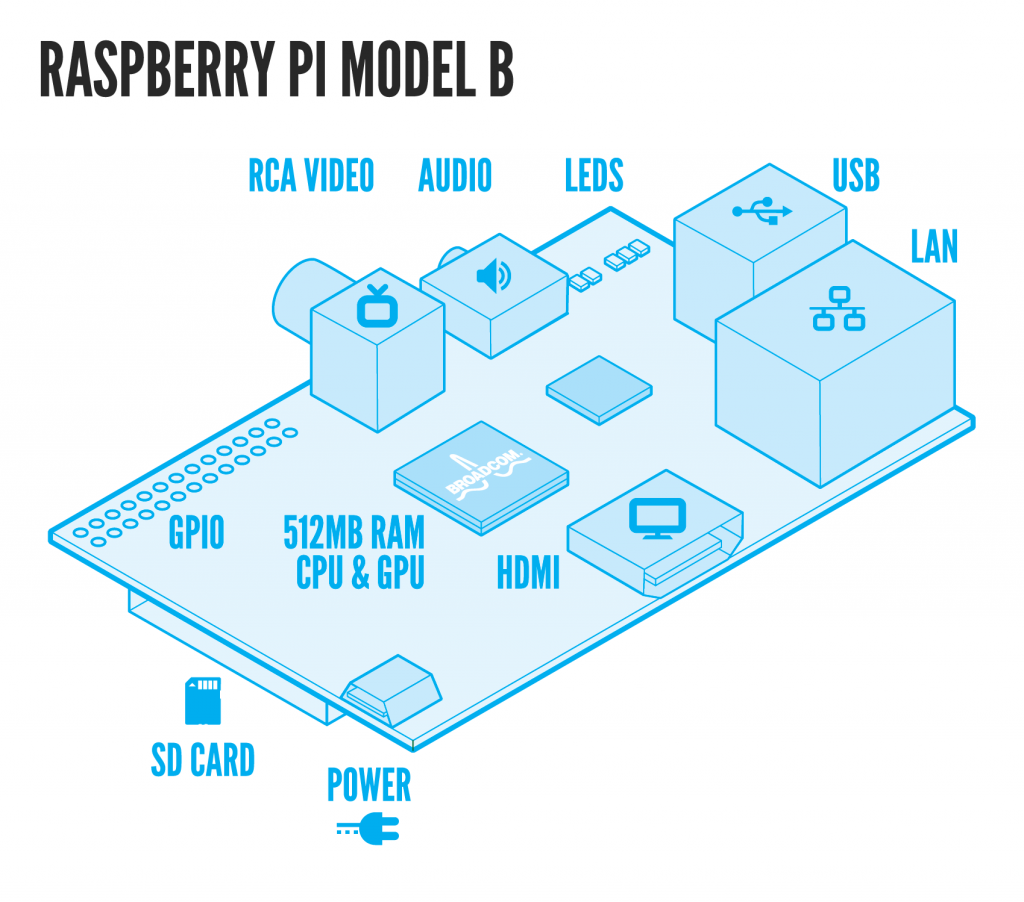
|
| Source: http://www.aoakley.com |
What cool things can you do with the Raspberry Pi?
Well, you can use it like a normal computer: word processing, surfing the internet, streaming videos, etc. You can write programs on it using the Idle software (Python language), Scratch, or Linux. This might seem mundane, but keep in mind that you bought this lil' computer for $40 freaking dollars (+shipping and handling). If you have kids, this is a seriously fantastic option for a first computer, especially because you won't mind as much when they spill apple juice all over it (or if you're like me and still spill apple juice on computers, this is a great option for a backup computer..).GPIO Pins!
By far the coolest way to use the Pi is to interface w/ the real world using the GPIO pins (that row of 26 pins adjacent to the RCA video port, or the yellow port). The GPIO pins have different functions as shown in the photo below: 17 of the 26 total pins are actual GPIO pins, while the rest are either ground, a power source (5 VDC or 3.3 VDC) or labeled "DNC" for "Do Not Connect"/"N/C" for "Not Connected" (connecting to these pins may short the Pi, so it is recommended to avoid these).
 |
| You can print this GPIO Leaf and stick in on the board! |
GPIO pins can be used as an input or an output. As an input, the pin can distinguish between two values: HIGH* and LOW. As an output, you can send an ON, or HIGH signal (3.3 VDC), or an OFF, or LOW signal (0 VDC). These pins can be used for tons of physical tasks, like turning on/off lights (Christmas light choreography, anyone??), controlling motors, reading sensors, and honestly pretty much anything you can conceive, as long as you build a proper circuit.
Some of the GPIO pins also have more specific functions, such as SDA (data line), SCL (clock), etc.; if you're reading this as a beginner don't worry about these just yet. When you find a project you're excited about you'll naturally learn these functions as necessary.
*High input threshold is a signal of ~ 1.8 VDC, although it can vary between 0.8 - 2.0 VDC. This means that any signal coming in to your GPIO pin that is above 0.8 VDC may be read as "HIGH" by the RPi.
Advanced users will be happy to know that you can modify many of the GPIO characteristics from software (this link also has the robust GPIO electrical specifications).
For absolute beginners, here are some helpful things to know about the GPIO pins:
 GPIO
pins operate on Direct Current (DC) voltage. Unless you want to see
smoke come out of the RPi, do NOT input Alternating Current (AC)
signals, like the one that comes out of the wall.
GPIO
pins operate on Direct Current (DC) voltage. Unless you want to see
smoke come out of the RPi, do NOT input Alternating Current (AC)
signals, like the one that comes out of the wall. Be very careful about what you connect to the GPIO pins. You will not be able to control a motor directly from a GPIO pin; in this instance, the GPIO pin functions as a switch, rather than the actual power for the motor. Here's a great tutorial on how to control a small motor.
Looking for more inspiration? Here's a general list of 25 cool things to do w/ your RPi! You can also Google "Raspberry Pi projects" or browse the Instructables website for RPi projects.
The next post will cover a simple circuit you can build and control w/ the Pi.